Citations
Citations are a way for you to get bounding box references and citation text for every field in your extraction.
You can enable citations in Studio in the Build tab for an extractor config under “Advanced options”. Or via API by setting the citationsEnabled option to true in the extraction config.
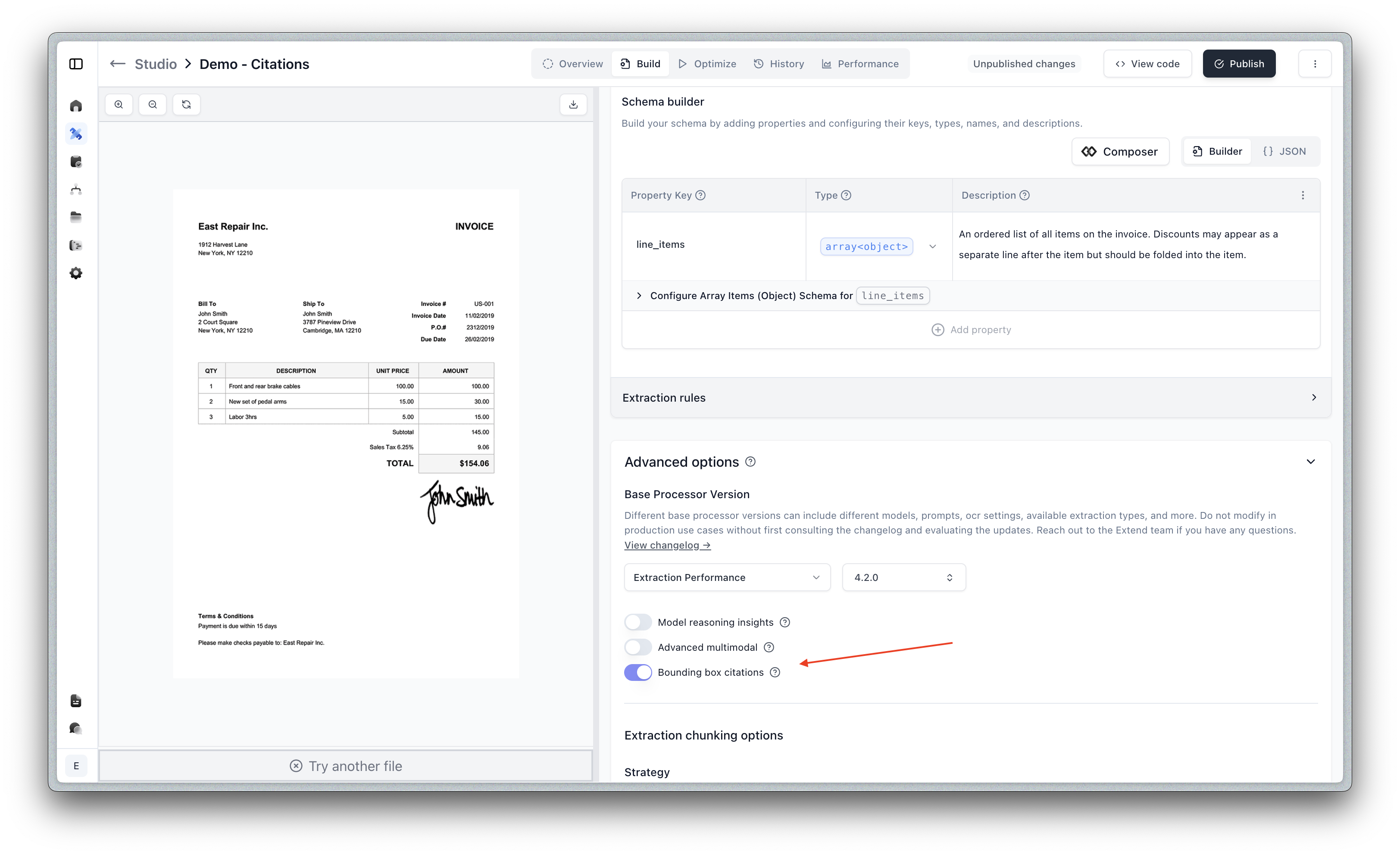
To generate robust and accurate citations, we use an additional citation focused model. As a result, using citations will add a moderate increase in latency on your use case.
Example
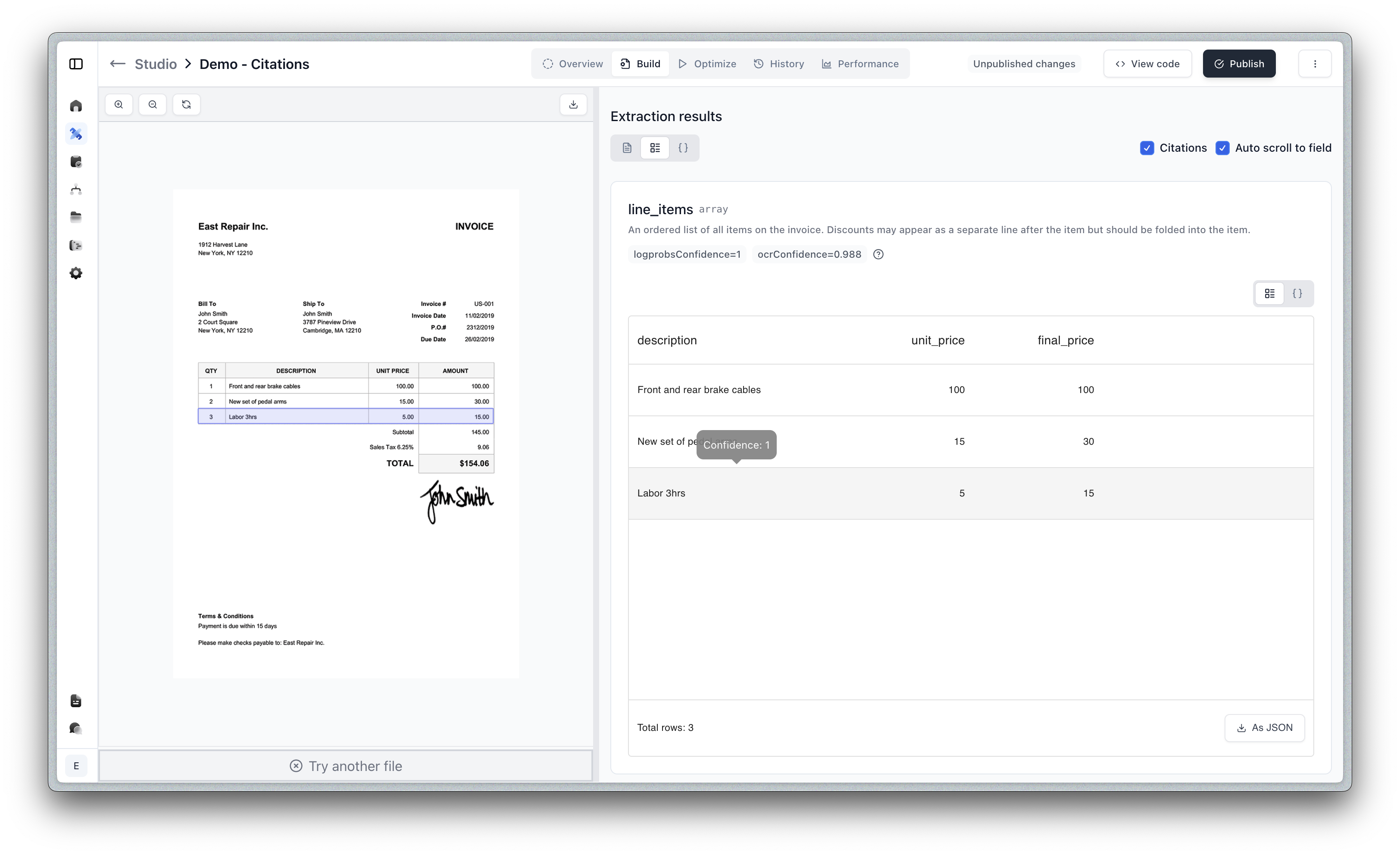
Citations are returned in the metadata object for each field. Learn more about Metadata here.
Citation Schema
The polygon and referenceText fields are only returned if the citationsEnabled option is enabled in the processor config. This can be enabled through the Studio in the Build tab under “Advanced options”.
The shape of the polygon is as follows:
How to use citations in pdf viewers
How to use the bounding values in order to place a bounding box on a file, depends heavily on the file type. In general though, you will need to take the bounding box values we return and convert them to whatever coordinate system your rendering library uses or what you define if you are using a native Canvas element approach to drawing them over an image for instance.
The values we return in the polygon field represent the coordinates of the bounding box on the image or page.
They indicate the points of the polygon that form the bounding box. You may need to convert these values into a format suitable for your rendering library.
If your rendering library uses a coordinate system based on percentages of the total image or page size, you would need to perform an additional conversion step.
For PDFs, here is an example of how to apply a transform to the value in order to be rendered using react-pdf-viewer or a similar library. The citation now includes page dimensions (width and height) directly in the page object:

