Running evaluation sets
Running well maintained and up to date evaluation sets is one of the best ways to ensure that your AI document processors are performing as expected and to identify areas for improvement, while iterating.
Follow this guide to learn more about how to run and maintain evaluation sets in Extend.
- There are two ways to run eval sets:
- Navigate to the runner page for the processor that has the evaluation set tied to it.
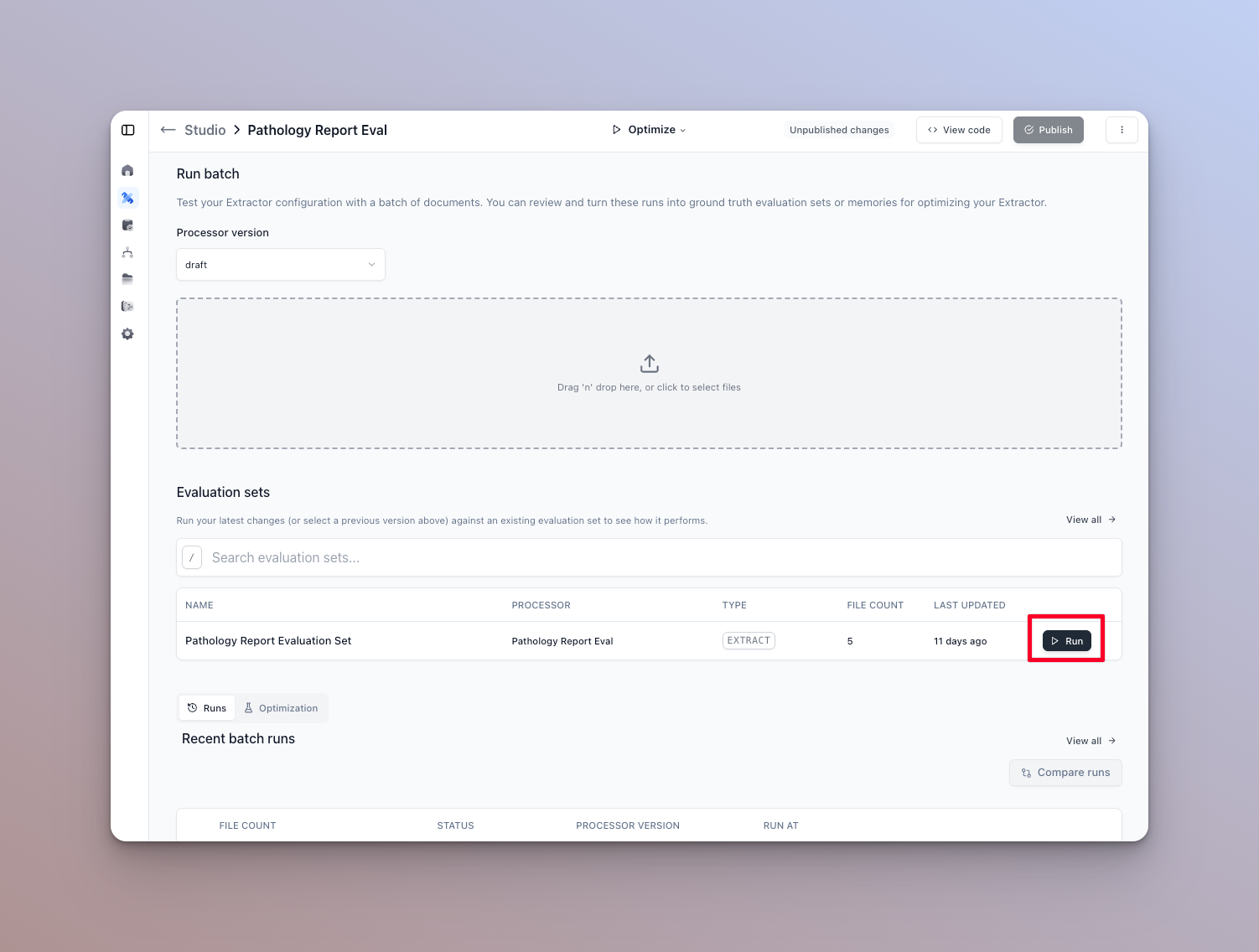
- Run the eval set from the eval set’s home page
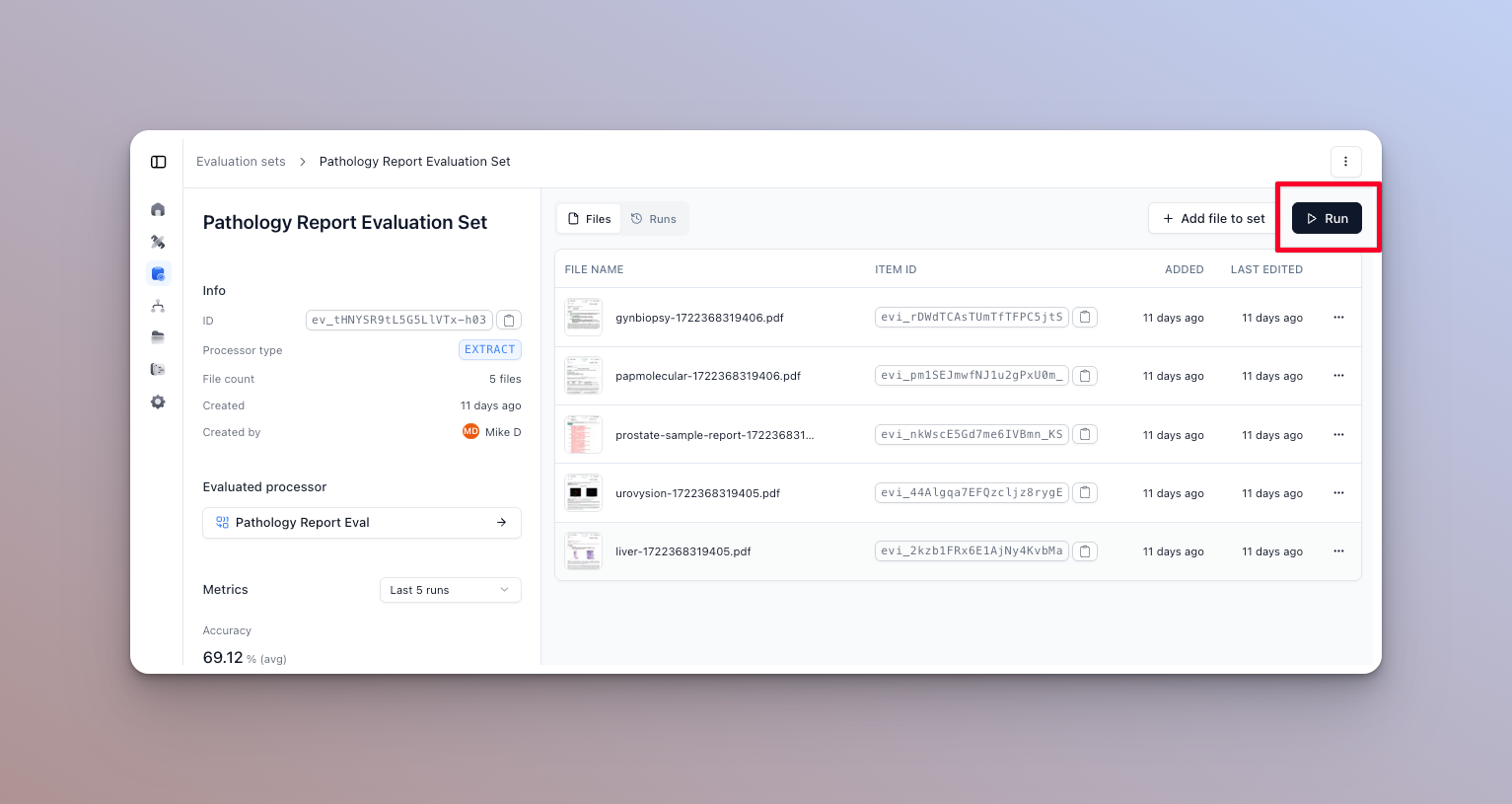
- Click the “Run” button on the evaluation set you want to run. This will open the run dialog.
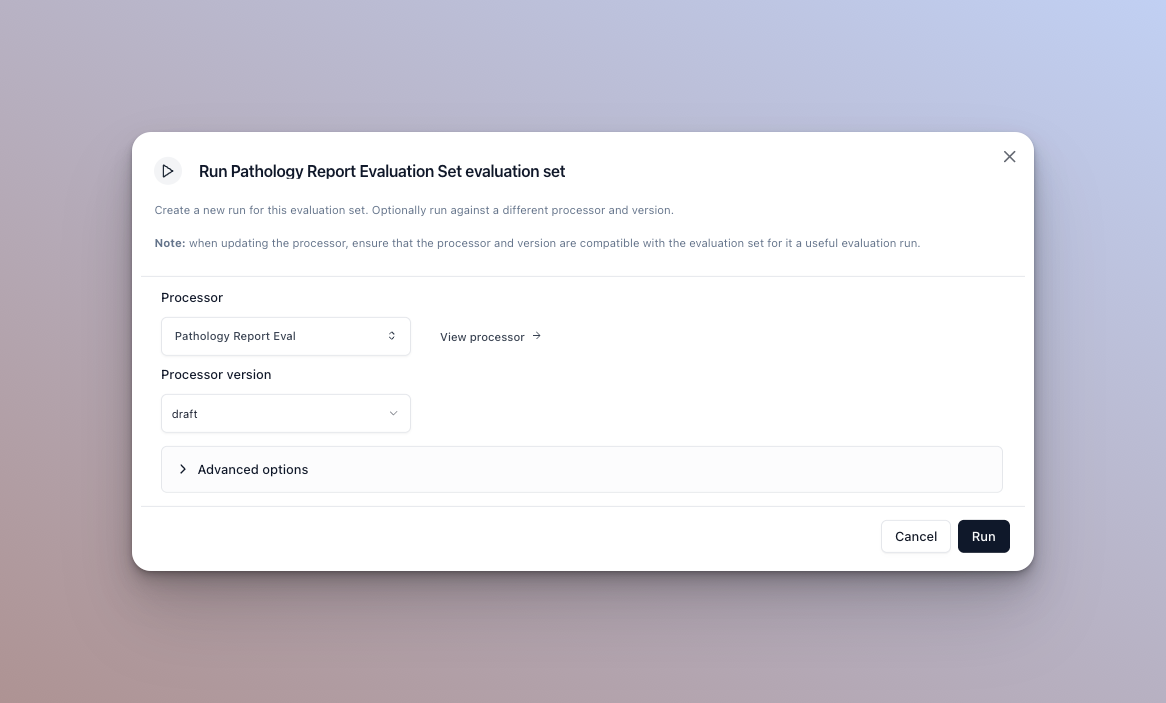
-
The default options are the processor and version you selected in the run ui. You can however update the version, or the actual processor before running here. See below for advanced option configuration
-
Click “Run Evaluation” to start the evaluation. You will be redirected to the evaluation run page where you can view the progress of the evaluation.
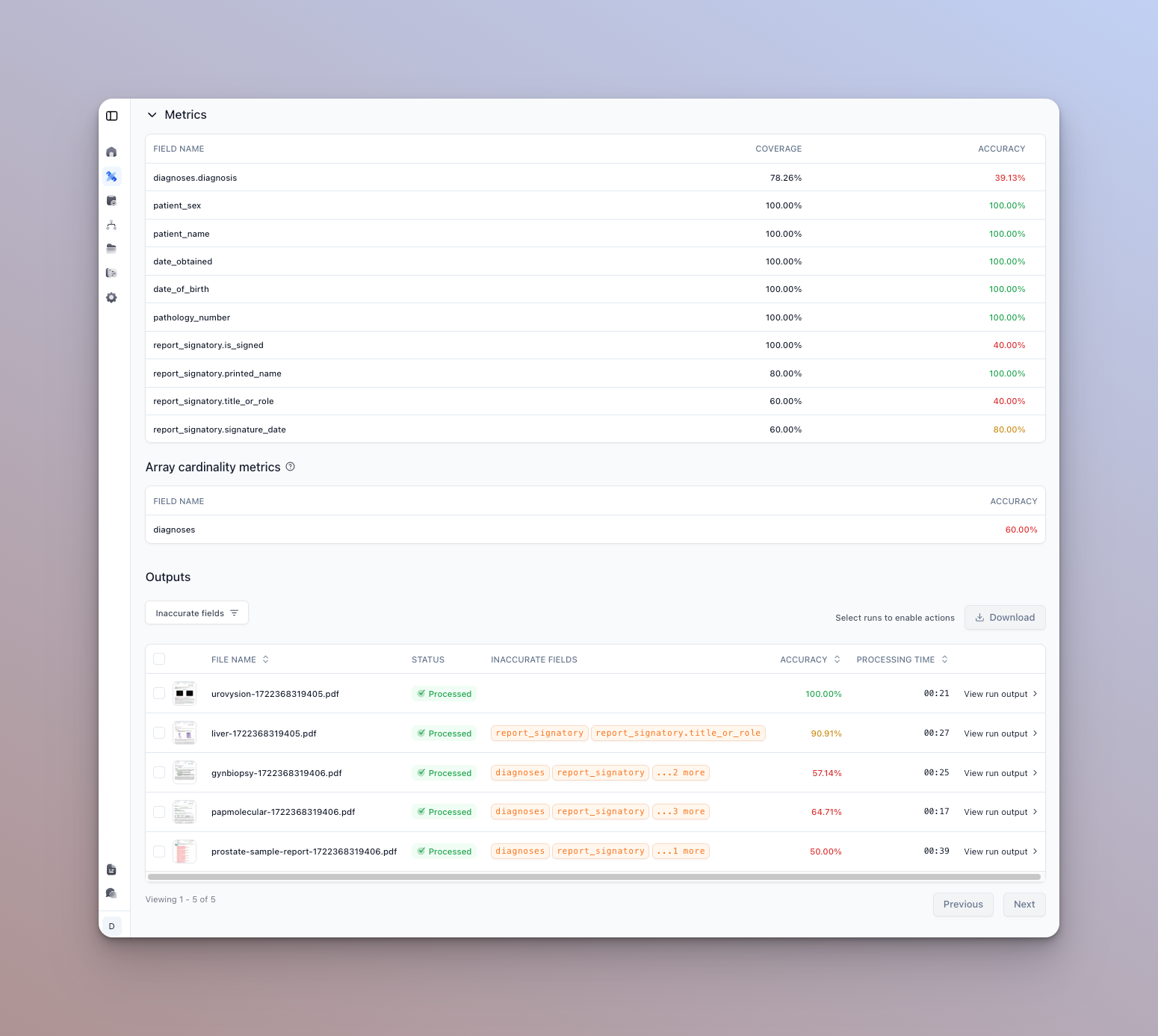
You can see a metrics summary at the top of the page, and a list of documents that were run and their results below.
Each processor type will have different metrics views. For instance a classification processor will show a per type accuracy distribution and a confusion matrix-like view.
- You can click on a given row to view the details of actual vs. expected outputs for that document.

- You can also download the results of the evaluation as a CSV file by clicking the Export button:
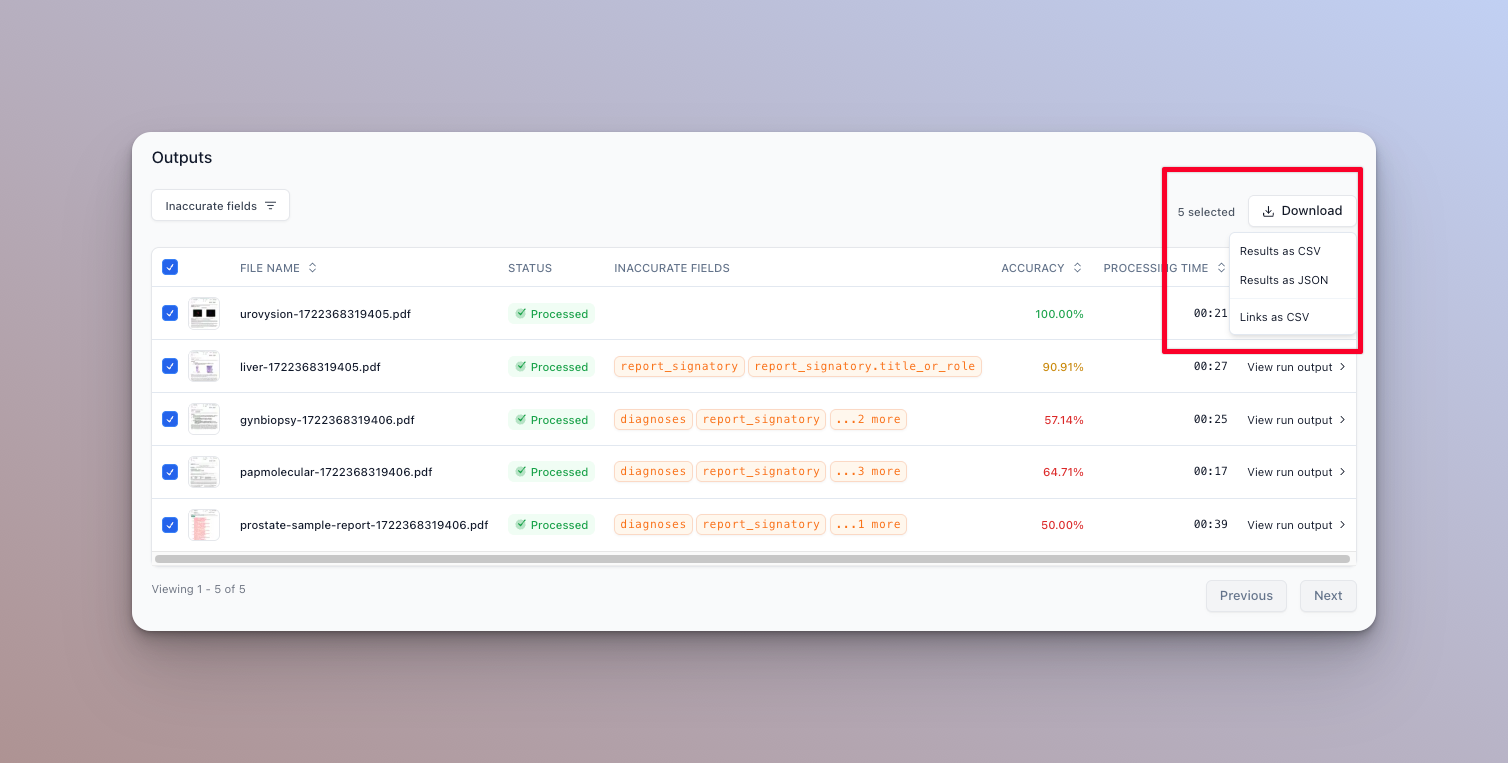
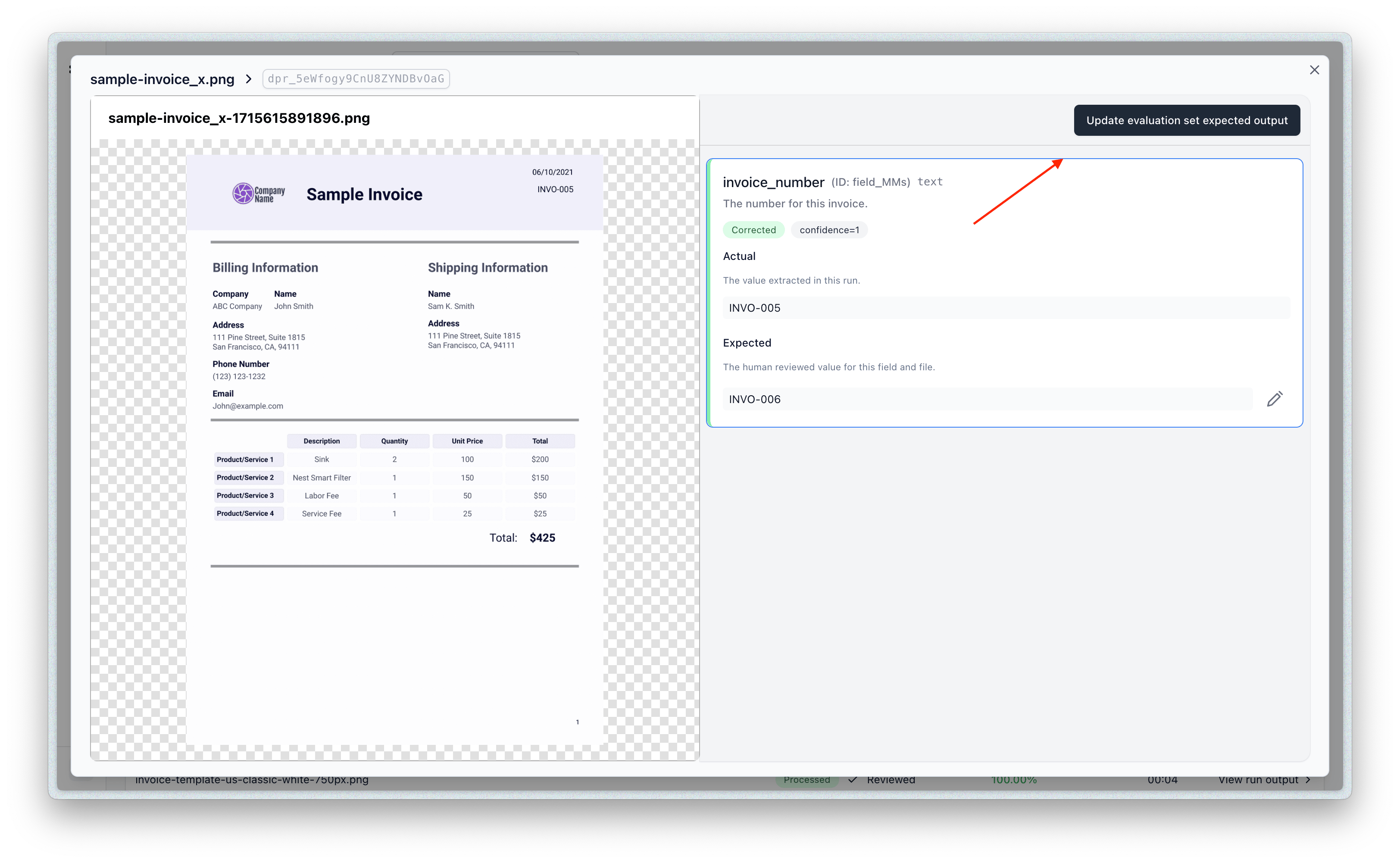
- You can also update the eval item to take the results of the evaluation as the new expected outputs by clicking the “Update” button:
Advanced options
There are a few advanced options you can configure when running an eval set that can affect how metrics are calculated.
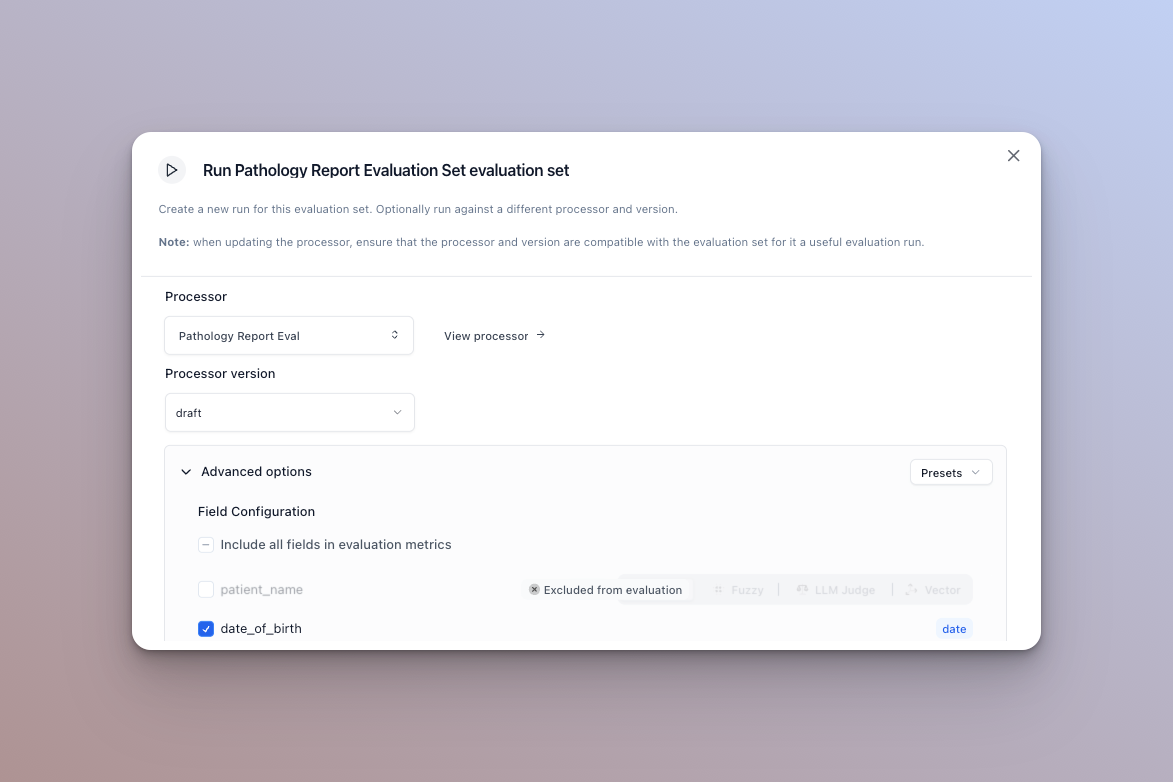
Excluding fields (extractors only)
If you want to exclude a field from the evaluation run’s metrics, simply uncheck the checkbox next to the field. The per document accuracy and overall accuracy will not take this field into account.
Matcher type (extractors only)
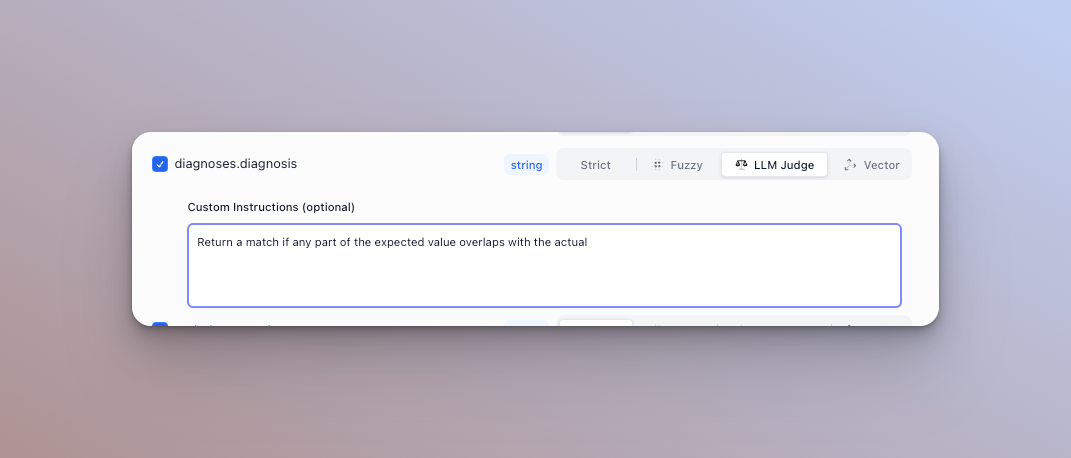
For string type fields, you can configure a custom matcher. There are four available to toggle from: strict, fuzzy, LLM judge, and vector.
Strict
The default matcher - checks for strict string equality and is case sensitive.
Fuzzy
Uses fuzzy matching distance which can allow for small errors between the actual and expected output. You can configure a threshold for what is considered a match (values above the threshold are a match). Uses a modified Levenshtein distance algorithm.
Recommended if you expect some variability, but only by a few characters.
LLM Judge
Passes the actual and expected output to an LLM and uses it to determine if they are semantically the same. By default, it can handle things like date formats (1/1/2025 vs Jan 1st 2025), abbreviations (St. vs Street), and numericals (1,000,000 vs one million). We highly recommend adding a custom instruction that acts as a rubric for the model to determine matches.
For example: Return true if and only if the expected and actual output have the same address, but you can ignore added or removed text.
Recommended if the extracted values are long sentences / paragraphs, or if you expect variability and want to define custom rules for matching
Vector
Embeds both the actual and expected value, and calculates the cosine similarity. Values that are more semantically similar will have a higher score (“house” and “home”). Values that are not semantically similar will have a lower score (“hot” and “cold”). You can configure a threshold for what is considered a match (values above the threshold are a match).
Recommended if you are trying to match based on the value’s meaning
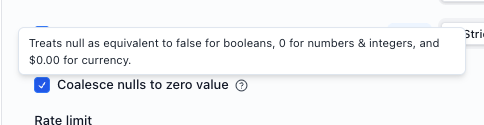
Null coalescing (extractors only)
For booleans, null and false will be treated as a match. For numbers, 0 and null will be treated as a match. For currency $0.00 and null will be a match.
Rate limits & file pre-processing cache (all processors)
The rate limit simply caps how many runs will be executed in a time period by this eval set run.
Clearing the pre-processing cache will re-run some pre-processing operations like chunking, metadata extraction, etc.
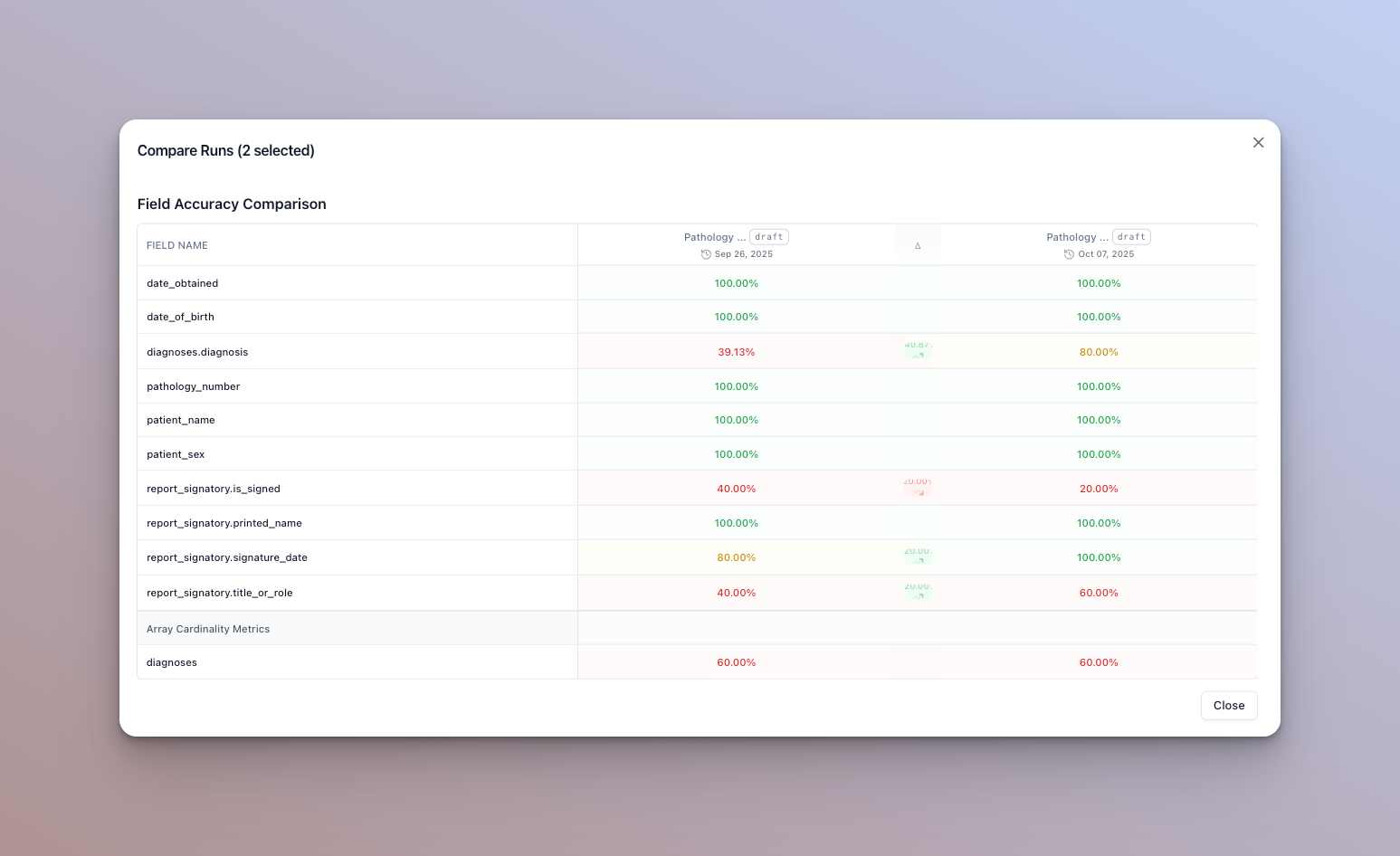
Compare accuracy across runs
To get a general idea of how your eval set is performing, you can compare accuracy across runs. Select the runs to compare and click “Compare runs” in the runs tab of the eval set home page.
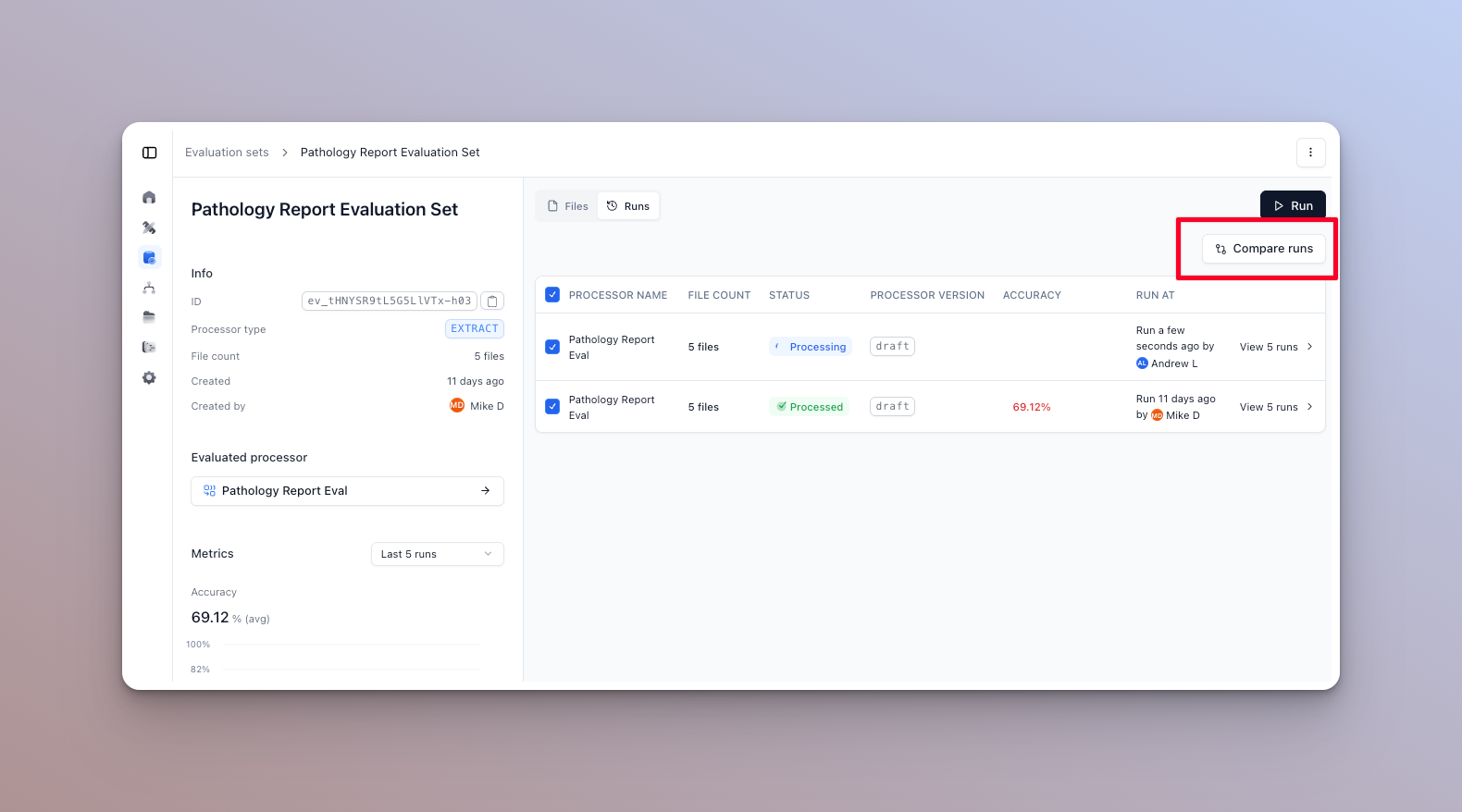
In this dialog, you can see color coded accuracy metrics, and whether they increased or decreased between runs. Hover over a column to see the exact change in percentage.